What is a vena cava stent?
If the blood no longer flows properly in the upper cavernous vein (the superior vena cava; VCS) may include shortness of breath, swelling of the face, neck or arms, headache, coughing and distension of the veins in the neck, chest and arms. To treat this blockage, a stent can be placed in the vein. A stent is a metal tube that keeps the vein open from the inside. The superior vena cava (VCS) is the large upper hollow vein that carries deoxygenated blood from the upper part of the body back to the heart. Vena cava stents are specifically designed for use in the body and are used to treat a narrowing (stenosis) or blockage in the vein. This blockage is usually caused by a malignant tumor. Symptoms usually diminish 48 hours after stent placement.
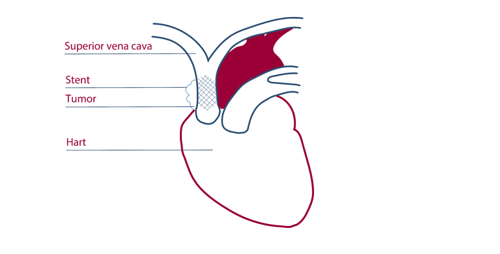
Illustration vena cava stent
 nl
nl