Ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer is a malignant tumor in one or both ovaries. Another word for ovary is ovary. That is why ovarian cancer is often called ovarian carcinoma.
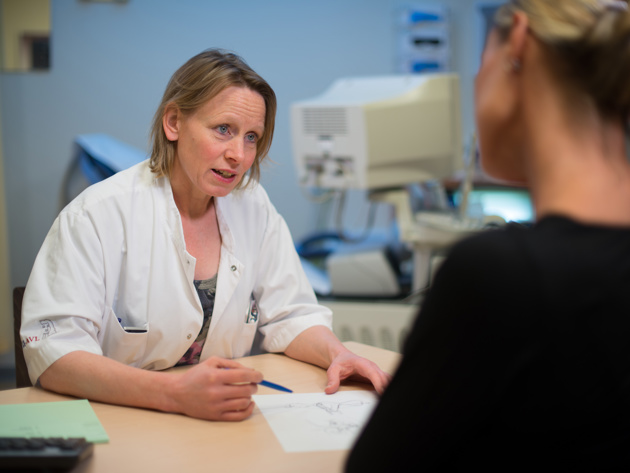
On this page you can read more about the symptoms, examinations and treatments for ovarian cancer.
Learn more about ovarian cancer
Causes of Ovarian Cancer
The cause of ovarian cancer is often not known. There are several types of ovarian cancer. The most common type starts in the fallopian tube. Sometimes there is a hereditary cause. However, this is only the case for a minority of women.
Symptoms of ovarian cancer
Ovarian cancer can spread without causing symptoms. As a result, it sometimes takes a long time before you notice something. Possible symptoms of ovarian cancer include:
- Bloated belly
- Feeling full quickly
- No hunger or appetite for food
- Nausea
- An annoying or pressing feeling at the bottom of the abdomen
- Needing to urinate more often than usual
Other possible complaints are:
- Gastrointestinal complaints, such as constipation or diarrhea
- Being very tired all the time
- Losing weight for no apparent reason
- Unexpected (abnormal) bleeding: blood loss after menopause, or blood loss between menstruations.
Hereditary ovarian cancer
Sometimes several people in a family have ovarian cancer. This is usually a coincidence, but can also be due to a hereditary cause: an abnormality in the DNA.
Metastatic ovarian cancer
A tumor in the ovaries can spread to other parts of the body. We call this metastatic ovarian cancer. The growth and spread of ovarian cancer is influenced by a number of factors, including the type of ovarian cancer and its stage of development.
The most common site for ovarian cancer metastases is the peritoneum, the thin membrane that lines the abdominal cavity and covers organs such as the uterus, intestines, and bladder.
Ovarian cancer that has spread through the body is also called metastatic ovarian cancer.
Waiting
We want to inform you as well as possible about the waiting time per condition. We do this based on a prognosis of the current waiting list. The waiting time can vary from patient to patient for various reasons. Your attending physician will give you more information during your outpatient consultation.
-
8 days
First appointment
This is approximately how long it will take until you have your first appointment
-
9 days
Rapid diagnostics
This is approximately how long it will take before you can start rapid diagnostics at the NKI
-
15 days
Second opinion
This is approximately how long it will take before you come in for a second opinion at the NKI
 nl
nl