Brain tumors - metastases
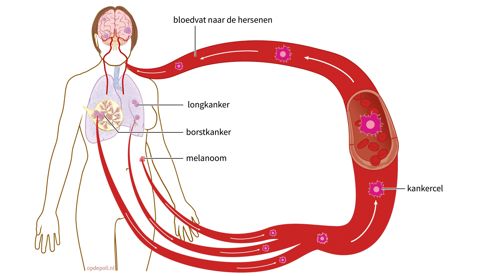
Metastases in the brain are also called brain metastases. These metastases are the result of a tumor that originated elsewhere in the body. The tumor usually starts in a certain part of the body, for example in the breast. In the event of a metastasis, this tumor spreads through the body through the blood and/or lymphs.
Learn more about brain metastases
Causes of metastases in the brain
10% to 40% of people with a solid tumor (cancer that originates in an organ or tissue) have to deal with metastases in the brain. The tumor cells end up in the small blood vessels of the brain. There they grow into tumors that can cause complaints. Metastases in the brain are much more common than a tumor that starts in the brain itself.
Metastases in the brain are more common in the last phase of a disease. Then there are often metastases further down the body, for example in the liver, bones or lungs.
All types of cancer can metastasize to the brain. For example, breast cancer, lung cancer and malignant skin cancer (melanoma).
Symptoms of metastases in the brain
The symptoms of a brain metastasis are different for everyone. That depends on the location of the metastasis in the brain. The symptoms may include:
- Headache
- Nausea and vomiting
- Paralysis of the arm, leg or one side of the body
- Balance problems
- Seizures
- Difficulty talking
- Difficulty seeing
- Different behavior and/or forgetfulness
Research & diagnosis
Your attending physician will determine in consultation with you which examinations are needed to make the diagnosis and draw up the treatment plan. All the tests and treatments mentioned can, but do not have to be applied. The examinations and treatments depend on your condition, age and the stage of the disease, among other things.
Waiting
We want to inform you as well as possible about the waiting time per condition. We do this based on a prognosis of the current waiting list. The waiting time can vary from patient to patient for various reasons. Your attending physician will give you more information during your outpatient consultation.
-
4 days
First appointment
This is approximately how long it will take until you have your first appointment
-
14 days
Surgery
We aim to remove malignant tumors within 14 days.
-
4 days
Second opinion
This is approximately how long it will take before you come in for a second opinion at the NKI
 nl
nl